目录
1.1 gsql的语法
1.2 gsql常用选项
1.2.1 最常用的必要选项
1.2.2 -r选项
1.2.3 -E选项
1.2.4 -t选项
1.2.5 -A选项
1.2.6 -v选项
1.2.7 -c选项
1.2.8 -f选项
1.2.9 -q选项
1.3 gsql的元命令
1.3.1 l命令
1.3.2 du命令和dg命令
1.3.3 db命令
1.3.4 dn命令
1.3.5 d命令
1.3.6 dt命令
1.3.7 di命令
1.3.8 dv命令
1.3.9 ds命令
1.3.10 df命令
1.3.11 d TableName命令
1.3.12 di IndexName命令
1.3.13 dx命令
1.3.14 x命令
1.3.15 timing命令
1.3.16 h命令
1.3.17 ?命令
1.3.18 ! os_command命令
1.3.19 o fileName命令
1.3.20 i file.sql命令
1.3.21 conninfo命令
1.3.22 c[onnect] [DBNAME]命令
1.3.23 echo [string]命令
1.3.24 q命令和快捷键ctrl+d
1.4 gsql初始化文件.gsqlrc
2.客户端安全
2.1配置客户端接入认证
2.2客户端验证
1.1 gsql的语法
gsql –help
[omm@test ~]$ gsql –help
gsql is the FusionInsight LibrA interactive terminal.
Usage:
gsql [OPTION]… [DBNAME [USERNAME]]
General options:
-c, –command=COMMAND run only single command (SQL or internal) and exit
-d, –dbname=DBNAME database name to connect to (default: “omm”)
-f, –file=FILENAME execute commands from file, then exit
-l, –list list available databases, then exit
-v, –set=, –variable=NAME=VALUE
set gsql variable NAME to VALUE
-V, –version output version information, then exit
-X, –no-gsqlrc do not read startup file (~/.gsqlrc)
-1 (“one”), –single-transaction
execute command file as a single transaction
-?, –help show this help, then exit
Input and output options:
-a, –echo-all echo all input from script
-e, –echo-queries echo commands sent to server
-E, –echo-hidden display queries that internal commands generate
-k, –with-key=KEY the key for decrypting the encrypted file
-L, –log-file=FILENAME send session log to file
-m, –maintenance can connect to cluster during 2-pc transaction recovery
-n, –no-libedit disable enhanced command line editing (libedit)
-o, –output=FILENAME send query results to file (or |pipe)
-q, –quiet run quietly (no messages, only query output)
-s, –single-step single-step mode (confirm each query)
-S, –single-line single-line mode (end of line terminates SQL command)
Output format options:
-A, –no-align unaligned table output mode
-F, –field-separator=STRING
set field separator (default: “|”)
-H, –html HTML table output mode
-P, –pset=VAR[=ARG] set printing option VAR to ARG (see pset command)
-R, –record-separator=STRING
set record separator (default: newline)
-r if this parameter is set,use libedit
-t, –tuples-only print rows only
-T, –table-attr=TEXT set HTML table tag attributes (e.g., width, border)
-x, –expanded turn on expanded table output
-z, –field-separator-zero
set field separator to zero byte
-0, –record-separator-zero
set record separator to zero byte
Connection options:
-h, –host=HOSTNAME database server host or socket directory (default: “/opt/gaussdbi/tmp”)
-p, –port=PORT database server port (default: “5432”)
-U, –username=USERNAME database user name (default: “omm”)
-W, –password=PASSWORD the password of specified database user
For more information, type “?” (for internal commands) or “help” (for SQL
commands) from within gsql, or consult the gsql section in the FusionInsight LibrA
documentation.
Report bugs to .
[omm@test ~]$
1.2 gsql常用选项
1.2.1 最常用的必要选项
使用gsql命令,用数据库用户student,连接到openGauss数据库管理系统下的studentdb数据库:
gsql -d studentdb -h 192.168.100.91 -U student -p 26000 -W student@ustb2020
[omm@test ~]$ gsql -d studentdb -h 192.168.100.91 -U student -p 26000 -W student@ustb2020
gsql ((openGauss 1.0.1 build 13b34b53) compiled at 2020-10-12 02:00:59 commit 0 last mr )
SSL connection (cipher: DHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256, bits: 128)
Type “help” for help.
studentdb=>
其中的选项说明如下:
-d选项: 指定gsql客户端连接的数据库
-h选项: 指定gsql客户端连接的服务器IP
-U选项: 指定gsql客户端连接数据库的用户名
-p选项: 指定gsql客户端连接的服务器端口号
-W选项: 指定gsql客户端连接的用户密码
1.2.2 -r选项
gsql -d studentdb -h 192.168.100.91 -U student -p 26000 -W student@ustb2020 -r
gsql命令的-r选项,第一个作用是当我们在gsql中执行了很多语句后,如果我们想重新执行之前执行过的语句,可以使用上箭头和下箭头,向前和向后翻阅之前执行过的命令和SQL语句。
执行下面的语句:使用上箭头可以提供很多便利性。
SELECT * FROM instructor WHERE salary=90000;
studentdb=> SELECT * FROM instructor WHERE salary=90000;
id | dept_name | name | salary
———-+——————+———+———-
12121 | Finance | Wu | 90000.00
(1 row)
studentdb=>
1.2.3 -E选项
-E选项会让gsql客户端程序再执行元命令的时候,显示其对应的SQL语句。
使用Linux用户omm,打开一个Linux终端窗口,执行gsql的元命令l,该命令的作用是显示当前系统有哪些数据库:
gsql -d studentdb -h 192.168.100.91 -U student -p 26000 -W student@ustb2020 -r -E
l
q
[omm@test ~]$ gsql -d studentdb -h 192.168.100.91 -U student -p 26000 -W student@ustb2020 -r -E
gsql ((openGauss 1.0.1 build 13b34b53) compiled at 2020-10-12 02:00:59 commit 0 last mr )
SSL connection (cipher: DHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256, bits: 128)
Type “help” for help.
studentdb=> l
********* QUERY ********** -E选项会显示gsql客户端的元命令对应的SQL语句
SELECT d.datname as “Name”,
pg_catalog.pg_get_userbyid(d.datdba) as “Owner”,
pg_catalog.pg_encoding_to_char(d.encoding) as “Encoding”,
d.datcollate as “Collate”,
d.datctype as “Ctype”,
pg_catalog.array_to_string(d.datacl, E’n’) AS “Access privileges”
FROM pg_catalog.pg_database d
ORDER BY 1;
**************************
List of databases
Name | Owner | Encoding | Collate | Ctype | Access privileges
———–+——-+———–+———+——-+——————-
postgres | omm | SQL_ASCII | C | C |
studentdb | omm | SQL_ASCII | C | C |
template0 | omm | SQL_ASCII | C | C | =c/omm +
| | | | | omm=CTc/omm
template1 | omm | SQL_ASCII | C | C | =c/omm +
| | | | | omm=CTc/omm
(4 rows)
studentdb=> q
[omm@test ~]$
如果不使用-E选项,同样执行上面的命令系列,结果如下:
gsql -d studentdb -h 192.168.100.91 -U student -p 26000 -W student@ustb2020 -r
l
q
[omm@test ~]$ gsql -d studentdb -h 192.168.100.91 -U student -p 26000 -W student@ustb2020 -r
gsql ((openGauss 1.0.1 build 13b34b53) compiled at 2020-10-12 02:00:59 commit 0 last mr )
SSL connection (cipher: DHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256, bits: 128)
Type “help” for help.
studentdb=> l
List of databases
Name | Owner | Encoding | Collate | Ctype | Access privileges
———–+——-+———–+———+——-+——————-
postgres | omm | SQL_ASCII | C | C |
studentdb | omm | SQL_ASCII | C | C |
template0 | omm | SQL_ASCII | C | C | =c/omm +
| | | | | omm=CTc/omm
template1 | omm | SQL_ASCII | C | C | =c/omm +
| | | | | omm=CTc/omm
(4 rows)
studentdb=> q
[omm@test ~]$
可以看出,如果没有-E选项,不会显示元命令l对应的SQL查询语句。
1.2.4 -t选项
-t选项会让gsql客户端程序在执行SQL查询语句的时候,返回的结果不显示列名及返回结果的行数。
使用Linux用户omm,打开一个Linux终端窗口,执行如下的命令:
gsql -d studentdb -h 192.168.100.91 -U student -p 26000 -W student@ustb2020 -r -t
select * from instructor where salary=80000;
[omm@test ~]$ gsql -d studentdb -h 192.168.100.91 -U student -p 26000 -W student@ustb2020 -r -t
gsql ((openGauss 1.0.1 build 13b34b53) compiled at 2020-10-12 02:00:59 commit 0 last mr )
SSL connection (cipher: DHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256, bits: 128)
Type “help” for help.
studentdb=> select * from instructor where salary=80000;
76543 | Finance | Singh | 80000.00
98345 | Elec. Eng. | Kim | 80000.00
studentdb=> q
[omm@test ~]$
1.2.5 -A选项
-A选项会让gsql客户端程序在执行SQL查询语句的时候,不对齐显示查询返回的行数据,如图6-7所示(列不是对齐的!)。
gsql -d studentdb -h 192.168.100.91 -U student -p 26000 -W student@ustb2020 -r -A
select * from instructor where salary=80000;
q
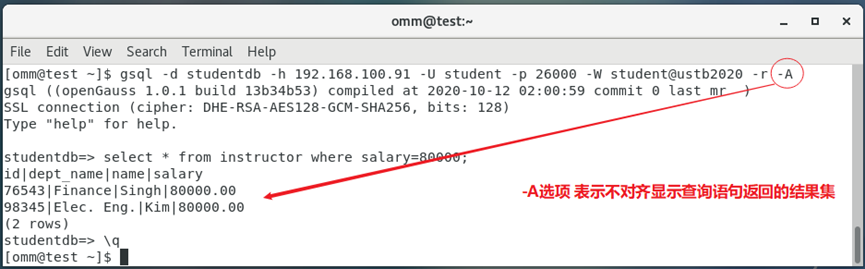
图6-8 -A选项表示不对齐显式
可以将-A和-t两个选项同时应用,表示不对齐显示,也不显示列名和返回行数:
gsql -d studentdb -h 192.168.100.91 -U student -p 26000 -W student@ustb2020 -r -At
select * from instructor where salary=80000;
q
[omm@test ~]$ gsql -d studentdb -h 192.168.100.91 -U student -p 26000 -W student@ustb2020 -r -At
gsql ((openGauss 1.0.1 build 13b34b53) compiled at 2020-10-12 02:00:59 commit 0 last mr )
SSL connection (cipher: DHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256, bits: 128)
Type “help” for help.
studentdb=> select * from instructor where salary=80000;
76543|Finance|Singh|80000.00
98345|Elec. Eng.|Kim|80000.00
studentdb=> q
[omm@test ~]$
1.2.6 -v选项
-v选项会让gsql客户端程序在命令行中设置gsql环境变量。
如果我们想在命令行中告诉gsql启动后关闭自动提交,设置为手动事务提交,可以执行如下命令:
gsql -d studentdb -h 192.168.100.91 -U student -p 26000 -W student@ustb2020
-v AUTOCOMMIT=off -r
[omm@test ~]$ gsql -d studentdb -h 192.168.100.91 -U student -p 26000 -W student@ustb2020
> -v AUTOCOMMIT=off -r
gsql ((openGauss 1.0.1 build 13b34b53) compiled at 2020-10-12 02:00:59 commit 0 last mr )
SSL connection (cipher: DHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256, bits: 128)
Type “help” for help.
studentdb=>
1.2.7 -c选项
-c选项会让gsql客户端程序直接在命令行中运行SQL语句,示例如下:
gsql -d studentdb -h 192.168.100.91 -U student -p 26000 -W student@ustb2020
-c “select * from instructor where salary=80000”
[omm@test ~]$ gsql -d studentdb -h 192.168.100.91 -U student -p 26000 -W student@ustb2020
> -c “select * from instructor where salary=80000”
id | dept_name | name | salary
———-+——————–+————+———-
76543 | Finance | Singh | 80000.00
98345 | Elec. Eng. | Kim | 80000.00
(2 rows)
[omm@test ~]$
1.2.8 -f选项
-f选项会让gsql客户端程序直接在命令行中直接运行SQL脚本文件。
首先用omm用户,生成一个测试用的SQL语句脚本:
cat > test.sql
select * from instructor where salary=80000;
EOF
[omm@test ~]$ cat > test.sql
> select * from instructor where salary=80000;
> EOF
[omm@test ~]$
然后使用gsql客户端程序在命令行中直接执行刚刚创建的SQL语句脚本:
gsql -d studentdb -h 192.168.100.91 -U student -p 26000 -W student@ustb2020 -f test.sql
rm test.sql
[omm@test ~]$ gsql -d studentdb -h 192.168.100.91 -U student -p 26000 -W student@ustb2020 -f test.sql
id | dept_name | name | salary
——-+————+——-+———-
76543 | Finance | Singh | 80000.00
98345 | Elec. Eng. | Kim | 80000.00
(2 rows)
total time: 0 ms
[omm@test ~]$ rm test.sql
[omm@test ~]$
1.2.9 -q选项
-q选项会让gsql客户端程序以安静的方式运行,只显示查询结果。
首先用omm用户,执行下面的gsql命令(使用了-q选项),创建test表,然后再次执行gsql命令(不使用-q选项),删除刚刚创建的test表,接着再次执行gsql命令(不使用-q选项),重新创建test表,最后又一次执行gsql命令(使用了-q选项),删除刚刚创建的test表:
gsql -d studentdb -h 192.168.100.91 -U student -p 26000 -W student@ustb2020
-c “create table test(col char)” -q
gsql -d studentdb -h 192.168.100.91 -U student -p 26000 -W student@ustb2020
-c “drop table test”
gsql -d studentdb -h 192.168.100.91 -U student -p 26000 -W student@ustb2020
-c “create table test(col char)”
gsql -d studentdb -h 192.168.100.91 -U student -p 26000 -W student@ustb2020
-c “drop table test” -q
[omm@test script]$ gsql -d studentdb -h 192.168.100.91 -U student -p 26000 -W student@ustb2020
> -c “create table test(col char)” -q
[omm@test script]$ gsql -d studentdb -h 192.168.100.91 -U student -p 26000 -W student@ustb2020
> -c “drop table test”
DROP TABLE
[omm@test script]$ gsql -d studentdb -h 192.168.100.91 -U student -p 26000 -W student@ustb2020
> -c “create table test(col char)”
CREATE TABLE
[omm@test script]$ gsql -d studentdb -h 192.168.100.91 -U student -p 26000 -W student@ustb2020
> -c “drop table test” -q
[omm@test script]$
我们发现使用了-q选项的gsql没有显示任何信息。
执行下面的命令,进行SQL查询,我们发现虽然有-q选项,但是会显示查询结果。
gsql -d studentdb -h 192.168.100.91 -U student -p 26000 -W student@ustb2020
-c “select * from instructor where salary=80000” -q
[omm@test script]$ gsql -d studentdb -h 192.168.100.91 -U student -p 26000 -W student@ustb2020
> -c “select * from instructor where salary=80000” -q
id | dept_name | name | salary
———-+———————+———-+———-
76543 | Finance | Singh | 80000.00
98345 | Elec. Eng. | Kim | 80000.00
(2 rows)
[omm@test script]$
1.3 gsql的元命令
本节的测试均使用下面的命令登录到openGauss数据库:
gsql -d studentdb -h 192.168.100.91 -U student -p 26000 -W student@ustb2020 -r
[omm@test ~]$ gsql -d studentdb -h 192.168.100.91 -U student -p 26000 -W student@ustb2020 -r
gsql ((openGauss 1.0.1 build 13b34b53) compiled at 2020-10-12 02:00:59 commit 0 last mr )
SSL connection (cipher: DHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256, bits: 128)
Type “help” for help.
studentdb=>
1.3.1 l命令
元命令l的作用是显示openGauss数据库集簇中,目前有哪些数据库:
l
studentdb=> l
List of databases
Name | Owner | Encoding | Collate | Ctype | Access privileges
———–+——-+———–+———+——-+——————-
postgres | omm | SQL_ASCII | C | C |
studentdb | omm | SQL_ASCII | C | C |
template0 | omm | SQL_ASCII | C | C | =c/omm +
| | | | | omm=CTc/omm
template1 | omm | SQL_ASCII | C | C | =c/omm +
| | | | | omm=CTc/omm
(4 rows)
studentdb=>
1.3.2 du命令和dg命令
元命令dg命令与元命令du命令的作用类似,都是显示openGauss数据库集簇中,目前有哪些用户和角色。
du
dg
studentdb=> du
List of roles
Role name | Attributes | Member of
———–+————————————————————————+———–
omm | Sysadmin, Create role, Create DB, Replication, Administer audit, UseFT | {}
student | Sysadmin | {}
studentdb=> dg
List of roles
Role name | Attributes | Member of
———–+————————————————————————+———–
omm | Sysadmin, Create role, Create DB, Replication, Administer audit, UseFT | {}
student | Sysadmin | {}
studentdb=>
1.3.3 db命令
元命令db的作用是显示openGauss数据库集簇中,目前有哪些表空间:
db
studentdb=> db
List of tablespaces
Name | Owner | Location
———————+———–+————————
pg_default | omm |
pg_global | omm |
student_ts | omm | tablespace/student_ts1
(3 rows)
studentdb=>
1.3.4 dn命令
元命令dn的作用是显示当前数据库,有哪些数据库模式:
dn
studentdb=> dn
List of schemas
Name | Owner
————–+————
cstore | omm
dbe_perf | omm
public | omm
snapshot | omm
(4 rows)
studentdb=>
1.3.5 d命令
元命令d的作用是显示当前数据库下的所有的数据库对象(相当于命令dtvsE,这里E表示外部表):
d
List of relations
Schema | Name | Type | Owner | Storage
———–+———————+———-+—————-+———————————-
public | advisor | table | student | {orientation=row,compression=no}
public | classroom | table | student | {orientation=row,compression=no}
public | course | table | student | {orientation=row,compression=no}
public | department | table | student | {orientation=row,compression=no}
public | instructor | table | student | {orientation=row,compression=no}
public | prereq | table | student | {orientation=row,compression=no}
public | section | table | student | {orientation=row,compression=no}
public | student | table | student | {orientation=row,compression=no}
public | takes | table | student | {orientation=row,compression=no}
public | teaches | table | student | {orientation=row,compression=no}
public | time_slot | table | student | {orientation=row,compression=no}
(11 rows)
studentdb=>
1.3.6 dt命令
元命令dt的作用是显示数据库中所有的表:
dt
studentdb=> dt
List of relations
Schema | Name | Type | Owner | Storage
——–+————+——-+———+———————————-
public | advisor | table | student | {orientation=row,compression=no}
public | classroom | table | student | {orientation=row,compression=no}
public | course | table | student | {orientation=row,compression=no}
public | department | table | student | {orientation=row,compression=no}
public | instructor | table | student | {orientation=row,compression=no}
public | prereq | table | student | {orientation=row,compression=no}
public | section | table | student | {orientation=row,compression=no}
public | student | table | student | {orientation=row,compression=no}
public | takes | table | student | {orientation=row,compression=no}
public | teaches | table | student | {orientation=row,compression=no}
public | time_slot | table | student | {orientation=row,compression=no}
(11 rows)
studentdb=>
元命令dt+的作用是以扩展的方式,显示数据库中所有的表:
dt+
studentdb=> dt+
List of relations
Schema | Name | Type | Owner | Size | Storage | Description
——–+————+——-+———+————+———————————-+————-
public | advisor | table | student | 8192 bytes | {orientation=row,compression=no} |
public | classroom | table | student | 8192 bytes | {orientation=row,compression=no} |
public | course | table | student | 8192 bytes | {orientation=row,compression=no} |
public | department | table | student | 8192 bytes | {orientation=row,compression=no} |
public | instructor | table | student | 8192 bytes | {orientation=row,compression=no} |
public | prereq | table | student | 8192 bytes | {orientation=row,compression=no} |
public | section | table | student | 8192 bytes | {orientation=row,compression=no} |
public | student | table | student | 8192 bytes | {orientation=row,compression=no} |
public | takes | table | student | 8192 bytes | {orientation=row,compression=no} |
public | teaches | table | student | 8192 bytes | {orientation=row,compression=no} |
public | time_slot | table | student | 8192 bytes | {orientation=row,compression=no} |
(11 rows)
studentdb=>
后面增加一个+号,表示显示更多的信息。
1.3.7 di命令
元命令di的作用是查看数据库中索引的信息:
di
studentdb=> di
List of relations
Schema | Name | Type | Owner | Table | Storage
——–+—————–+——-+———+————+———
public | advisor_pkey | index | student | advisor |
public | classroom_pkey | index | student | classroom |
public | course_pkey | index | student | course |
public | department_pkey | index | student | department |
public | instructor_pkey | index | student | instructor |
public | prereq_pkey | index | student | prereq |
public | section_pkey | index | student | section |
public | student_pkey | index | student | student |
public | takes_pkey | index | student | takes |
public | teaches_pkey | index | student | teaches |
public | time_slot_pkey | index | student | time_slot |
(11 rows)
studentdb=>
1.3.8 dv命令
元命令di的作用是查看数据库中索引的信息。
测试数据集目前暂时没有视图,因此首先创建一个视图:
create or replace view faculty as
select ID, name, dept_name
from instructor;
studentdb=> create or replace view faculty as
studentdb-> select ID, name, dept_name
studentdb-> from instructor;
CREATE VIEW
studentdb=>
执行gsql元命令dv,查询当前数据库下有哪些视图:
dv
studentdb=> dv
List of relations
Schema | Name | Type | Owner | Storage
————-+————-+——+———+———
public | faculty | view | student |
(1 row)
studentdb=>
删除刚刚创建的视图:
drop view faculty;
studentdb=> drop view faculty;
DROP VIEW
studentdb=>
1.3.9 ds命令
元命令ds的作用是查看数据库中序列的信息。
测试数据集目前暂时没有序列,因此首先创建一个表,其两列都是序列,创建该表会自动创建2个序列:
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS test;
create table test(id serial primary key,testnum serial);
studentdb=> DROP TABLE IF EXISTS test;
NOTICE: table “test” does not exist, skipping
DROP TABLE
studentdb=> create table test(id serial primary key,testnum serial);
NOTICE: CREATE TABLE will create implicit sequence “test_id_seq” for serial column “test.id”
NOTICE: CREATE TABLE will create implicit sequence “test_testnum_seq” for serial column “test.testnum”
NOTICE: CREATE TABLE / PRIMARY KEY will create implicit index “test_pkey” for table “test”
CREATE TABLE
studentdb=>
执行gsql元命令ds,查询当前数据库下有哪些序列:
ds
studentdb=> ds
List of relations
Schema | Name | Type | Owner | Storage
——–+——————+———-+———+———
public | test_id_seq | sequence | student |
public | test_testnum_seq | sequence | student |
(2 rows)
studentdb=>
删除刚刚创建的测试表,序列也同时被删除,使用ds命令已经查不到有任何序列了:
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS test;
ds
studentdb=> DROP TABLE IF EXISTS test;
DROP TABLE
studentdb=> ds
No relations found.
studentdb=>
1.3.10 df命令
元命令df的作用是查看数据库中关于存储函数的信息。
因为目前数据库中暂时没有任何函数,首先执行下面的语句,创建一个测试用的函数:
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION myfunction(s INT)
RETURN INT
AS
BEGIN
IF(s>0) THEN
RETURN 1;
ELSEIF(s
RETURN -1;
ELSE
RETURN 0;
END IF;
END
/
studentdb=> CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION myfunction(s INT)
studentdb-> RETURN INT
studentdb-> AS
studentdb$> BEGIN
studentdb$> IF(s>0) THEN
studentdb$> RETURN 1;
studentdb$> ELSEIF(s
studentdb$> RETURN -1;
studentdb$> ELSE
studentdb$> RETURN 0;
studentdb$> END IF;
studentdb$> END
studentdb$> /
CREATE FUNCTION
studentdb=>
然后执行元命令df,查看当前数据库下有什么函数:
df
studentdb=> df
List of functions
Schema | Name | Result data type | Argument data types | Type | fencedmode | propackage
————-+———————+———————–+——————————+————-+——————+——————
public | myfunction | integer | s integer | normal | f | f
(1 row)
studentdb=>
删除用于测试的函数:
drop function myfunction;
df
studentdb=> drop function myfunction;
DROP FUNCTION
studentdb=> df
List of functions
Schema | Name | Result data type | Argument data types | Type | fencedmode | propackage
————-+———+————————+—————————–+——–+——————-+—————
(0 rows)
studentdb=>
1.3.11 d TableName命令
元命令d TableName的作用是查看某个表的信息。
执行下面的命令,查看表instructor的信息:
d instructor
studentdb=> d instructor
Table “public.instructor”
Column | Type | Modifiers
———–+———————–+———–
id | character varying(5) | not null
dept_name | character varying(20) |
name | character varying(20) | not null
salary | numeric(8,2) |
Indexes:
“instructor_pkey” PRIMARY KEY, btree (id) TABLESPACE student_ts
Foreign-key constraints:
“fk_sys_c0011280” FOREIGN KEY (dept_name) REFERENCES department(dept_name) ON UPDATE RESTRICT ON DELETE RESTRICT
Referenced by:
TABLE “teaches” CONSTRAINT “fk_sys_c0011287” FOREIGN KEY (id) REFERENCES instructor(id) ON UPDATE RESTRICT ON DELETE RESTRICT
TABLE “advisor” CONSTRAINT “fk_sys_c0011297” FOREIGN KEY (id) REFERENCES instructor(id) ON UPDATE RESTRICT ON DELETE RESTRICT
studentdb=>
可以看到,显示表的信息包括表的列名及数据类型、索引、外键、以及被哪个表引用。如果表不在数据库默认的表空间,还将显示表所在的表空间。这一点可以做个测试:
CREATE TABLESPACE test_ts RELATIVE LOCATION ‘tablespace/test_ts1’;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS test;
CREATE TABLE test(col1 smallint) TABLESPACE test_ts;
d test
drop table test;
drop tablespace test_ts;
studentdb=> CREATE TABLESPACE test_ts RELATIVE LOCATION ‘tablespace/test_ts1’;
CREATE TABLESPACE
studentdb=> DROP TABLE IF EXISTS test;
NOTICE: table “test” does not exist, skipping
DROP TABLE
studentdb=> CREATE TABLE test(col1 smallint) TABLESPACE test_ts;
CREATE TABLE
studentdb=> d test
Table “public.test”
Column | Type | Modifiers
——–+———-+———–
col1 | smallint |
Tablespace: “test_ts” (因为表test不在数据库的默认表空间中,因此显示表test所在的表空间)
studentdb=> drop table test;
DROP TABLE
studentdb=> drop tablespace test_ts;
DROP TABLESPACE
studentdb=>
1.3.12 di IndexName命令
元命令di IndexName的作用是查看某个索引的信息。
执行下面的元命令,查看当前数据库下有哪些索引:
di
studentdb=> di
List of relations
Schema | Name | Type | Owner | Table | Storage
——–+—————–+——-+———+————+———
public | advisor_pkey | index | student | advisor |
public | classroom_pkey | index | student | classroom |
public | course_pkey | index | student | course |
public | department_pkey | index | student | department |
public | instructor_pkey | index | student | instructor |
public | prereq_pkey | index | student | prereq |
public | section_pkey | index | student | section |
public | student_pkey | index | student | student |
public | takes_pkey | index | student | takes |
public | teaches_pkey | index | student | teaches |
public | time_slot_pkey | index | student | time_slot |
(11 rows)
studentdb=>
执行下面的元命令,显示索引instructor_pkey的详细信息:
di instructor_pkey
studentdb=> di instructor_pkey
List of relations
Schema | Name | Type | Owner | Table | Storage
————-+—————————–+——-+———+————+———
public | instructor_pkey | index | student | instructor |
(1 row)
studentdb=>
1.3.13 dx命令
元命令dx的作用是查看已安装的扩展程序信息。
dx
studentdb=> dx
List of installed extensions
Name | Version | Schema | Description
—————-+————+———————+————————————————-
mot_fdw | 1.0 | pg_catalog | foreign-data wrapper for MOT access
plpgsql | 1.0 | pg_catalog | PL/pgSQL procedural language
(2 rows)
studentdb=>
1.3.14 x命令
元命令x的语法: x [ on | off | auto ]
元命令dx的作用是设置语句的输出模式。默认情况下记录上按行的方式来显示的。如果执行元命令x on,则显示将按每条记录每列的方式来显示。这种方式在有些情况下很有用。
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS test;
create table test(id int,name varchar(20));
insert into test values(1,’zqf’),(2,’zfz’);
select * from test;
x on
select * from test;
x off
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS test;
studentdb=> DROP TABLE IF EXISTS test;
DROP TABLE
studentdb=> create table test(id int,name varchar(20));
CREATE TABLE
studentdb=> insert into test values(1,’zqf’),(2,’zfz’);
INSERT 0 2
studentdb=> select * from test; 默认情况下,查询语句的显示方式为行方式
id | name
—-+——
1 | zqf
2 | zfz
(2 rows)
studentdb=> x on 修改显示方式为列方式
Expanded display is on.
studentdb=> select * from test;
-[ RECORD 1 ]
id | 1
name | zqf
-[ RECORD 2 ]
id | 2
name | zfz
studentdb=> x off 修改显示方式为行方式
Expanded display is off.
studentdb=> DROP TABLE IF EXISTS test;
DROP TABLE
studentdb=>
1.3.15 timing命令
元命令timing的语法: timing [ on | off ]
元命令timing的作用是,如果设置为on,将显示SQL语句的执行时间。
select * from instructor where salary=80000;
timing on
select * from instructor where salary=80000;
timing off
studentdb=> select * from instructor where salary=80000;
id | dept_name | name | salary
——-+————+——-+———-
76543 | Finance | Singh | 80000.00
98345 | Elec. Eng. | Kim | 80000.00
(2 rows)
studentdb=> timing on
Timing is on.
studentdb=> select * from instructor where salary=80000;
id | dept_name | name | salary
——-+————+——-+———-
76543 | Finance | Singh | 80000.00
98345 | Elec. Eng. | Kim | 80000.00
(2 rows)
Time: 0.436 ms
studentdb=> timing off
Timing is off.
studentdb=>
1.3.16 h命令
元命令h的作用是获取SQL语句的帮助。例如我们想获取update语句的帮助信息:
h update
studentdb=> h update
Command: UPDATE
Description: update rows of a table
Syntax:
UPDATE [ ONLY ] table_name [ * ] [ [ AS ] alias ]
SET {column_name = { expression | DEFAULT } |
( column_name [, …] ) = {( { expression | DEFAULT } [, …] ) |sub_query }
}[, …]
[ FROM from_list] [ WHERE condition ]
[ RETURNING {* | {output_expression [ [ AS ] output_name ]} [, …] }];
studentdb=>
想获取insert语句的帮助信息:
h insert
studentdb=> h insert
Command: INSERT
Description: create new rows in a table
Syntax:
[ WITH [ RECURSIVE ] with_query [, …] ]
INSERT INTO table_name [ ( column_name [, …] ) ]
{ DEFAULT VALUES | VALUES {( { expression | DEFAULT } [, …] ) }[, …] | query }
[ ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE { column_name = { expression | DEFAULT } } [, …] ]
[ RETURNING {* | {output_expression [ [ AS ] output_name ] }[, …]} ];
studentdb=>
1.3.17 ?命令
元命令?的作用是获取gsql元命令的帮助。
?
studentdb=> ?
General
copyright show FusionInsight LibrA usage and distribution terms
g [FILE] or ; execute query (and send results to file or |pipe)
h(help) [NAME] help on syntax of SQL commands, * for all commands
parallel [on [num]|off] toggle status of execute (currently off)
q quit gsql
Query Buffer
e [FILE] [LINE] edit the query buffer (or file) with external editor
ef [FUNCNAME [LINE]] edit function definition with external editor
p show the contents of the query buffer
r reset (clear) the query buffer
w FILE write query buffer to file
Input/Output
copy … perform SQL COPY with data stream to the client host
echo [STRING] write string to standard output
i FILE execute commands from file
i+ FILE KEY execute commands from encrypted file
ir FILE as i, but relative to location of current script
ir+ FILE KEY as i+, but relative to location of current script
o [FILE] send all query results to file or |pipe
qecho [STRING] write string to query output stream (see o)
Informational
(options: S = show system objects, + = additional detail)
d[S+] list tables, views, and sequences
d[S+] NAME describe table, view, sequence, or index
da[S] [PATTERN] list aggregates
db[+] [PATTERN] list tablespaces
dc[S+] [PATTERN] list conversions
dC[+] [PATTERN] list casts
dd[S] [PATTERN] show object descriptions not displayed elsewhere
ddp [PATTERN] list default privileges
dD[S+] [PATTERN] list domains
ded[+] [PATTERN] list data sources
det[+] [PATTERN] list foreign tables
des[+] [PATTERN] list foreign servers
deu[+] [PATTERN] list user mappings
dew[+] [PATTERN] list foreign-data wrappers
df[antw][S+] [PATRN] list [only agg/normal/trigger/window] functions
dF[+] [PATTERN] list text search configurations
dFd[+] [PATTERN] list text search dictionaries
dFp[+] [PATTERN] list text search parsers
dFt[+] [PATTERN] list text search templates
dg[+] [PATTERN] list roles
di[S+] [PATTERN] list indexes
dl list large objects, same as lo_list
dL[S+] [PATTERN] list procedural languages
dm[S+] [PATTERN] list materialized views
dn[S+] [PATTERN] list schemas
do[S] [PATTERN] list operators
dO[S+] [PATTERN] list collations
dp [PATTERN] list table, view, and sequence access privileges
drds [PATRN1 [PATRN2]] list per-database role settings
ds[S+] [PATTERN] list sequences
dt[S+] [PATTERN] list tables
dT[S+] [PATTERN] list data types
du[+] [PATTERN] list roles
dv[S+] [PATTERN] list views
dE[S+] [PATTERN] list foreign tables
dx[+] [PATTERN] list extensions
l[+] list all databases
sf[+] FUNCNAME show a function’s definition
z [PATTERN] same as dp
Formatting
a toggle between unaligned and aligned output mode
C [STRING] set table title, or unset if none
f [STRING] show or set field separator for unaligned query output
H toggle HTML output mode (currently off)
pset NAME [VALUE] set table output option
(NAME := {format|border|expanded|fieldsep|fieldsep_zero|footer|null|
numericlocale|recordsep|recordsep_zero|tuples_only|title|tableattr|pager})
t [on|off] show only rows (currently off)
T [STRING] set HTML


























































 到【灌水乐园】发言
到【灌水乐园】发言










三桥798:
bp和ss连用,di和es连用,和ds连用的是si
游戏开发小Y:
文章写的很详细,条理清晰,很容易看进去,学到了很多知识,感谢博主分享,支持博主
三桥798:
查看内存中的内容是d命令,选项是C选项
源码技术栈:
博主文章写的十分细致,结构严谨。感谢博主分享,期待博主持续输出好文,同时也希望可以来我博客指导我一番!
九九归二:
优质好文,博主的文章细节很到位,兼顾实用性和可操作性,感谢博主的分享,文章思路清晰,图文并茂,详略得当,必须支持,期待博主持续输出好文!