前言
日常的业务开发项目中只会配置一套数据源,如果需要获取其他系统的数据往往是通过调用接口, 或者是通过第三方工具比如kettle将数据同步到自己的数据库中进行访问。
但是也会有需要在项目中引用多数据源的场景。比如如下场景:
- 自研数据迁移系统,至少需要新、老两套数据源,从老库读取数据写入新库
- 自研读写分离中间件,系统流量增加,单库响应效率降低,引入读写分离方案,写入数据是一个数据源,读取数据是另一个数据源
某系统除了需要从自己的主要数据库上读取和管理数据外,还有一部分业务涉及到其他多个数据库,要求可以在任何方法上可以灵活指定具体要操作的数据库。
为了在开发中以最简单的方法使用,本文基于注解和AOP的方法实现,在spring boot框架的项目中,添加本文实现的代码类后,只需要配置好数据源就可以直接通过注解使用,简单方便。
一、原理
关键类说明
忽略掉controller/service/entity/mapper/xml介绍。
- jdbc.properties: 数据源配置文件。虽然可以配置到Spring boot的默认配置文件application.properties/application.yml文件当中,但是如果数据源比较多的话,根据实际使用,最佳的配置方式还是独立配置比较好。
- DynamicDataSourceConfig:数据源配置类
- DynamicDataSource:动态数据源配置类
- DataSourceRouting:动态数据源注解
- DynamicDataSourceAspect:动态数据源设置切面
- DynamicDataSourceContextHolder:当前线程持有的数据源key
- DataSourceConstants:数据源key常量类
开发流程
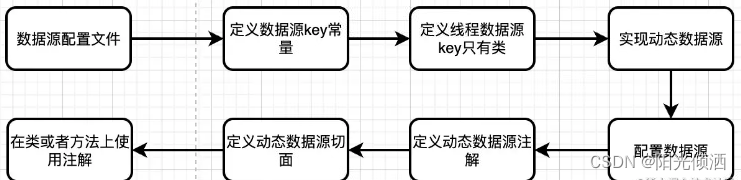
动态数据源流程
Spring Boot 的动态数据源,本质上是把多个数据源存储在一个 Map 中,当需要使用某个数据源时,从 Map 中获取此数据源进行处理。
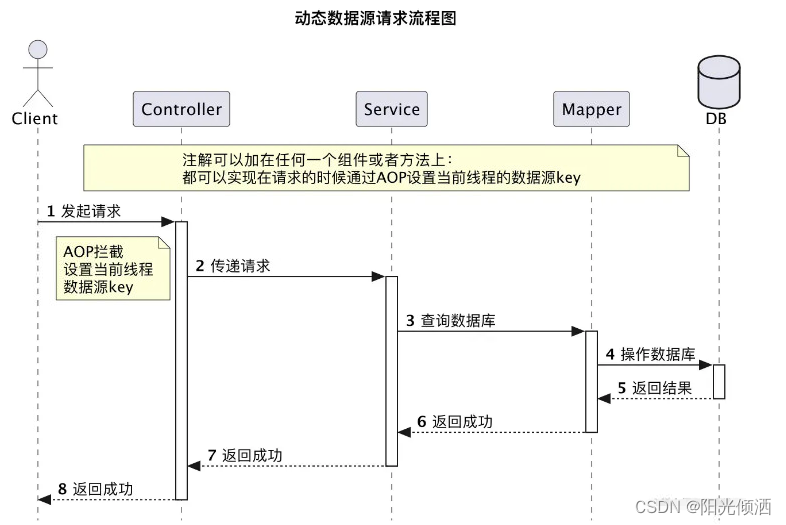
在 Spring 中已提供了抽象类 AbstractRoutingDataSource 来实现此功能,继承AbstractRoutingDataSource类并覆写其determineCurrentLookupKey()方法即可,该方法只需要返回数据源key即可,也就是存放数据源的Map的key。
因此,我们在实现动态数据源的,只需要继承它,实现自己的获取数据源逻辑即可。AbstractRoutingDataSource顶级继承了DataSource,所以它也是可以做为数据源对象,因此项目中使用它作为主数据源。
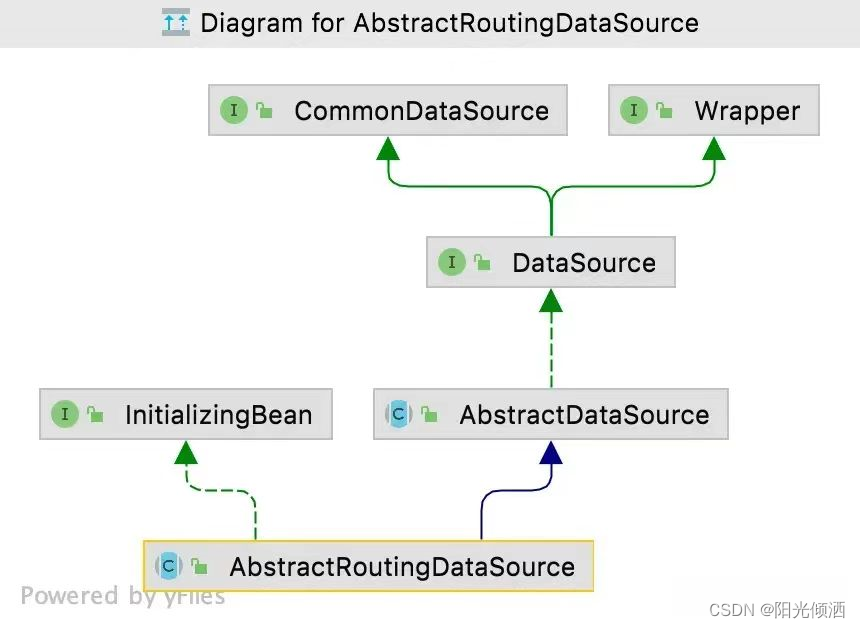
AbstractRoutingDataSource原理
AbstractRoutingDataSource中有一个重要的属性:
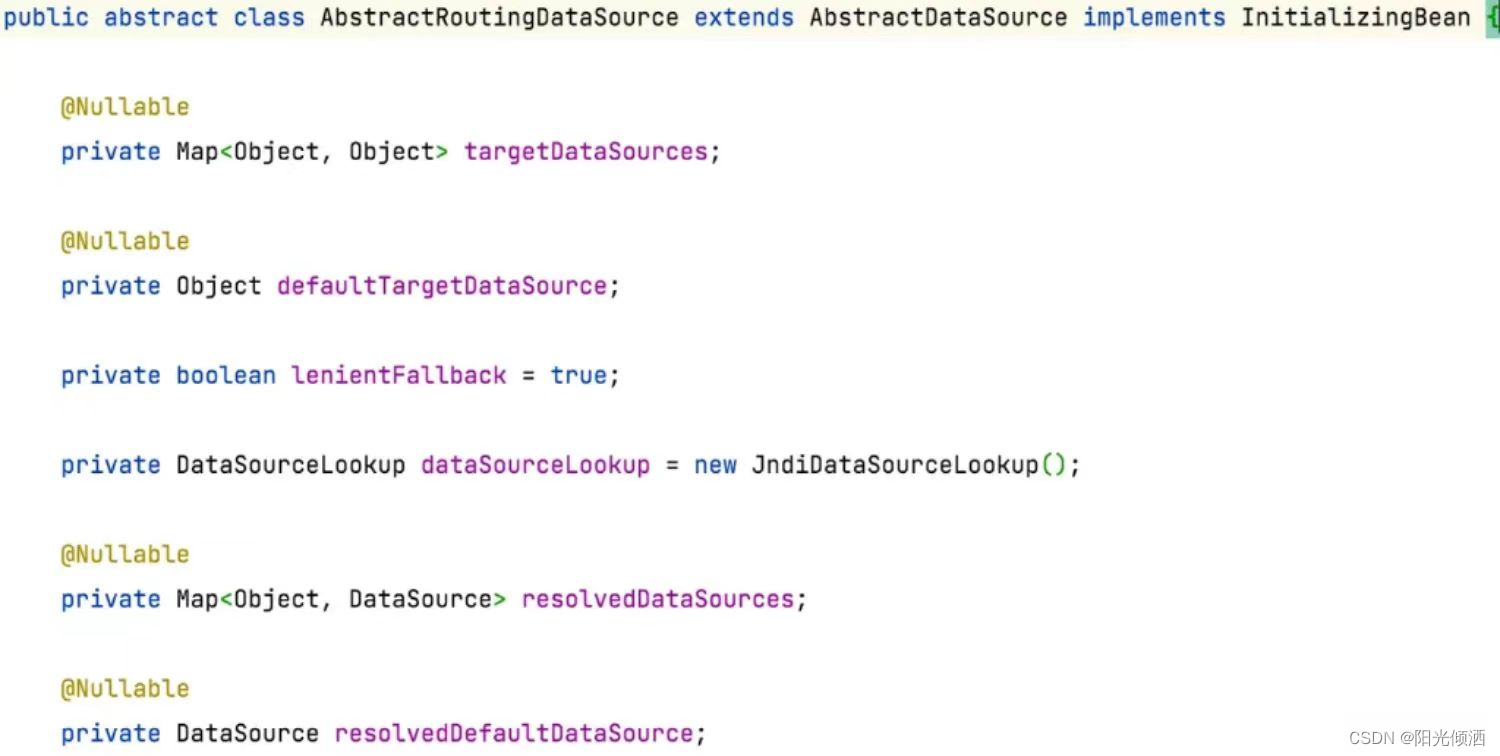
- argetDataSources:目标数据源,即项目启动的时候设置的需要通过AbstractRoutingDataSource管理的数据源。
- defaultTargetDataSource:默认数据源,项目启动的时候设置的默认数据源,如果没有指定数据源,默认返回改数据源。
- resolvedDataSources:也是存放的数据源,是对targetDataSources进行处理后进行存储的。可以看一下源码。
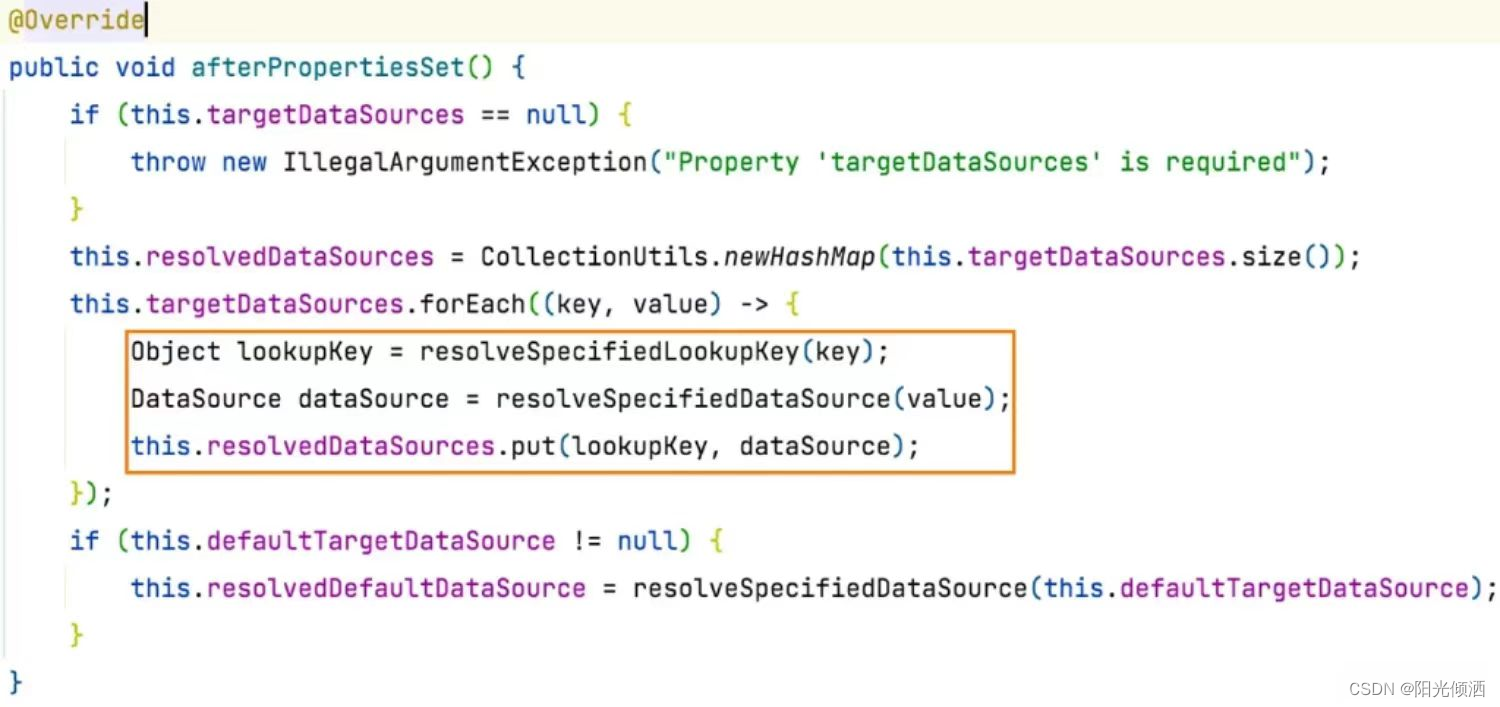
- resolvedDefaultDataSource: 对默认数据源进行了二次处理,源码如上图最后的两行代码。
AbstractRoutingDataSource中所有的方法和属性:
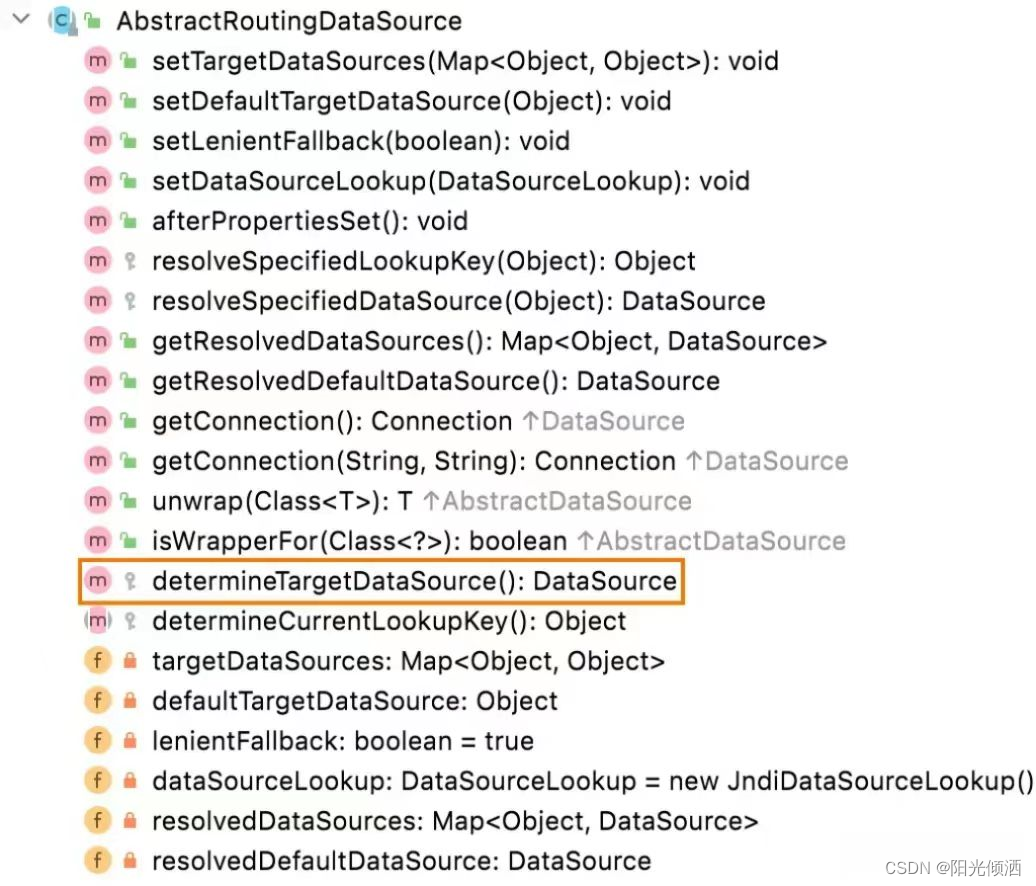
比较重要的是determineTargetDataSource方法。
protected DataSource determineTargetDataSource() {
Assert.notNull(this.resolvedDataSources, "DataSource router not initialized");
Object lookupKey = determineCurrentLookupKey();
DataSource dataSource = this.resolvedDataSources.get(lookupKey);
if (dataSource == null && (this.lenientFallback || lookupKey == null)) {
dataSource = this.resolvedDefaultDataSource;
}
if (dataSource == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot determine target DataSource for lookup key [" + lookupKey + "]");
}
return dataSource;
}
/**
* Determine the current lookup key. This will typically be
* implemented to check a thread-bound transaction context.
* Allows for arbitrary keys. The returned key needs
* to match the stored lookup key type, as resolved by the
* {@link #resolveSpecifiedLookupKey} method.
*/
@Nullable
protected abstract Object determineCurrentLookupKey();
这个方法主要就是返回一个DataSource对象,主要逻辑就是先通过方法determineCurrentLookupKey获取一个Object对象的lookupKey,然后通过这个lookupKey到resolvedDataSources中获取数据源(resolvedDataSources就是一个Map,上面已经提到过了);如果没有找到数据源,就返回默认的数据源。determineCurrentLookupKey就是程序员配置动态数据源需要自己实现的方法。
二、实现
引入Maven依赖
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-parent
2.1.10.RELEASE
UTF-8
UTF-8
1.8
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-configuration-processor
tk.mybatis
mapper-spring-boot-starter
2.1.5
mysql
mysql-connector-java
runtime
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-jdbc
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-aop
io.springfox
springfox-swagger-ui
2.9.2
io.springfox
springfox-swagger2
2.9.2
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-security
io.jsonwebtoken
jjwt
0.9.1
com.alibaba
fastjson
1.2.70
org.projectlombok
lombok
true
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-maven-plugin
org.mybatis.generator
mybatis-generator-maven-plugin
1.3.6
${basedir}/src/main/resources/generator/generatorConfig.xml
true
true
mysql
mysql-connector-java
5.1.41
tk.mybatis
mapper
4.1.5
主要实现步骤:一配置二使用
- 启动类注册动态数据源
- 配置文件中配置多个数据源
- 在需要的方法上使用注解指定数据源
-
1、在启动类添加 @Import({DynamicDataSourceRegister.class, MProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration.class})
// 注册动态多数据源
@Import({DynamicDataSourceRegister.class})
@MapperScan("com.yibo.mapper")//扫描Mapper接口
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class,args);
}
}
- 2、配置文件配置内容为:
# 默认数据源
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/user_center?useUnicode=true&useJDBCCompliantTimezoneShift=true&useLegacyDatetimeCode=false&serverTimezone=UTC
spring.datasource.hikari.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.hikari.username=root
spring.datasource.hikari.password=yibo
# 更多数据源
custom.datasource.names=ds1,ds2
custom.datasource.ds1.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
custom.datasource.ds1.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/content_center?useUnicode=true&useJDBCCompliantTimezoneShift=true&useLegacyDatetimeCode=false&serverTimezone=UTC
custom.datasource.ds1.username=root
custom.datasource.ds1.password=yibo
custom.datasource.ds2.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
custom.datasource.ds2.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/trade?useUnicode=true&useJDBCCompliantTimezoneShift=true&useLegacyDatetimeCode=false&serverTimezone=UTC
custom.datasource.ds2.username=root
custom.datasource.ds2.password=yibo
mybatis.type-aliases-package: com.yibo.center.domain.entity
mybatis.mapper-locations: classpath:mapper/*.xml
mapper.identity: MYSQL
mapper.not-empty: false
#是否激活 swagger true or false
swagger.enable=true
- 3、使用方法
import com.yibo.center.domain.entity.Share;
import com.yibo.datasource.anno.TargetDataSource;
import com.yibo.mapper.ShareMapper;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import java.util.List;
@Service
public class ShareService {
@Autowired
private ShareMapper shareMapper;
@TargetDataSource(name = "ds1")
@Transactional
public List findAll(){
return shareMapper.selectAll();
}
}
import com.yibo.center.domain.entity.TradeGoods;
import com.yibo.center.domain.vo.TradeGoodsAO;
import com.yibo.datasource.anno.TargetDataSource;
import com.yibo.mapper.TradeGoodsMapper;
import org.springframework.beans.BeanUtils;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @Description:
*/
@Service
public class TradeGoodsService {
@Autowired
private TradeGoodsMapper tradeGoodsMapper;
@TargetDataSource(name = "ds2")
@Transactional
public List findAll(){
return tradeGoodsMapper.selectAll();
}
@TargetDataSource(name = "ds2")
@Transactional
public String addTradeGoods(TradeGoodsAO tradeGoodsAO){
TradeGoods tradeGoods = new TradeGoods();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(tradeGoodsAO,tradeGoods);
tradeGoods.setAddTime(new Date());
tradeGoodsMapper.insert(tradeGoods);
return "SUCCESS";
}
}
import com.yibo.center.domain.entity.User;
import com.yibo.center.domain.vo.UserAo;
import com.yibo.mapper.UserMapper;
import org.springframework.beans.BeanUtils;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @Description:
*/
@Service
public class UserService {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
public List findAll(){
return userMapper.selectAll();
}
@Transactional
public User findById(Integer id){
User user = new User();
user.setId(id);
return userMapper.selectOne(user);
}
@Transactional
public String addUser(UserAo userAo){
User user = new User();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(userAo,user);
user.setCreateTime(new Date());
user.setUpdateTime(new Date());
userMapper.insert(user);
return "SUCCESS";
}
}
要注意的是,在使用MyBatis时,注解@TargetDataSource 不能直接在接口类Mapper上使用。
请将下面几个类放到Spring Boot项目中。
- DynamicDataSource.java
- DynamicDataSourceAspect.java
- DynamicDataSourceContextHolder.java
- DynamicDataSourceRegister.java
- TargetDataSource.java
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.lookup.AbstractRoutingDataSource;
/**
* @Description: 继承Spring AbstractRoutingDataSource实现路由切换
*/
public class DynamicDataSource extends AbstractRoutingDataSource {
@Override
protected Object determineCurrentLookupKey() {
return DynamicDataSourceContextHolder.getDataSourceType();
}
}
import com.yibo.datasource.DynamicDataSourceContextHolder;
import com.yibo.datasource.anno.TargetDataSource;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @Description: 动态数据源通知
*/
@Aspect
//保证该AOP在@Transactional之前执行
@Order(-1)
@Component
@Slf4j
public class DynamicDataSourceAspect {
/**
* @Description 在方法执行之前执行 @annotation(ds) 会拦截有ds这个注解的方法即有 TargetDataSource这个注解的
* @param @param point
* @param @param ds
* @param @throws Throwable 参数
* @return void 返回类型
* @throws
*/
@Before("@annotation(ds)")
public void changeDataSource(JoinPoint point, TargetDataSource ds)
throws Throwable {
String dsId = ds.name();
if (!DynamicDataSourceContextHolder.containsDataSource(dsId)) {
log.error("数据源[{}]不存在,使用默认数据源 > {}", ds.name(), point.getSignature());
}
else {
log.debug("Use DataSource : {} > {}", ds.name(),point.getSignature());
DynamicDataSourceContextHolder.setDataSourceType(ds.name());
}
}
/**
* @Description 在方法执行之后执行 @annotation(ds) 会拦截有ds这个注解的方法即有 TargetDataSource这个注解的
* @param @param point
* @param @param ds 参数
* @return void 返回类型
* @throws
*/
@After("@annotation(ds)")
public void restoreDataSource(JoinPoint point, TargetDataSource ds) {
log.debug("Revert DataSource : {} > {}", ds.name(), point.getSignature());
DynamicDataSourceContextHolder.clearDataSourceType();
}
}
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @Description: 动态数据源上下文管理
*/
public class DynamicDataSourceContextHolder {
//存放当前线程使用的数据源类型信息
private static final ThreadLocal contextHolder = new ThreadLocal();
//存放数据源id
public static List dataSourceIds = new ArrayList();
//设置数据源
public static void setDataSourceType(String dataSourceType) {
contextHolder.set(dataSourceType);
}
//获取数据源
public static String getDataSourceType() {
return contextHolder.get();
}
//清除数据源
public static void clearDataSourceType() {
contextHolder.remove();
}
/**
* 判断指定DataSrouce当前是否存在
*
* @param dataSourceId
* @return
*/
public static boolean containsDataSource(String dataSourceId){
return dataSourceIds.contains(dataSourceId);
}
}
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.MutablePropertyValues;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionRegistry;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.GenericBeanDefinition;
import org.springframework.boot.jdbc.DataSourceBuilder;
import org.springframework.context.EnvironmentAware;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import org.springframework.core.type.AnnotationMetadata;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* @Description: 注册动态数据源
* 初始化数据源和提供了执行动态切换数据源的工具类
* EnvironmentAware(获取配置文件配置的属性值)
*/
@Slf4j
public class DynamicDataSourceRegister implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar, EnvironmentAware {
//指定默认数据源(springboot2.0默认数据源是hikari如何想使用其他数据源可以自己配置)
private static final String DATASOURCE_TYPE_DEFAULT = "com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource";
//默认数据源
private DataSource defaultDataSource;
//用户自定义数据源
private Map customDataSources = new HashMap();
/**
* 加载多数据源配置
* @param env
*/
@Override
public void setEnvironment(Environment env) {
initDefaultDataSource(env);
initCustomDataSources(env);
}
/**
* 初始化主数据源
* @param env
*/
private void initDefaultDataSource(Environment env) {
// 读取主数据源
Map dsMap = new HashMap();
dsMap.put("driver", env.getProperty("spring.datasource.hikari.driver-class-name"));
dsMap.put("url", env.getProperty("spring.datasource.url"));
dsMap.put("username", env.getProperty("spring.datasource.hikari.username"));
dsMap.put("password", env.getProperty("spring.datasource.hikari.password"));
defaultDataSource = buildDataSource(dsMap);
}
/**
* 初始化更多数据源
* @param env
*/
private void initCustomDataSources(Environment env) {
// 读取配置文件获取更多数据源
String dsPrefixs = env.getProperty("custom.datasource.names");
for (String dsPrefix : dsPrefixs.split(",")) {
// 多个数据源
Map dsMap = new HashMap();
dsMap.put("driver", env.getProperty("custom.datasource." + dsPrefix + ".driver-class-name"));
dsMap.put("url", env.getProperty("custom.datasource." + dsPrefix + ".url"));
dsMap.put("username", env.getProperty("custom.datasource." + dsPrefix + ".username"));
dsMap.put("password", env.getProperty("custom.datasource." + dsPrefix + ".password"));
DataSource ds = buildDataSource(dsMap);
customDataSources.put(dsPrefix, ds);
}
}
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
Mapimport java.lang.annotation.*;
/**
* @Description: 作用于类、接口或者方法上
*/
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface TargetDataSource {
String name();
}
本文代码博主是经过测试后没有问题才发出来共享给大家的。对于连接池参数配置会应用到所有数据源上。
比如配置一个:
spring.datasource.maximum-pool-size=80
那么我们所有的数据源都会自动应用上。
补充:
如果你使用的是SpringMVC,并集成了Shiro,一般按网上的配置你可能是:
那么你请不要这样做,请按下面方法配置:


