- 👏作者简介:大家好,我是冰点,从业11年,目前在物流独角兽企业从事技术方面工作,
- 🍂博主正在努力完成2023计划中:以梦为马,扬帆起航,2023追梦人
- 📝联系方式:iceicepip,加我进群,大家一起学习,一起进步👀
文章目录
- 0.前言
- 1. 执行逻辑梳理
- 2. 核心源码解析
-
- 2.1. 准备阶段
- 2.2. 应用上下文创建阶段
- 2.3. 刷新上下文阶段
0.前言
背景:最近有位开发同学说面试被问到Spring Boot 的启动流程,以及被问到Spring Boot 的嵌入式Web容器是什么时候加载的。如何加载的。是怎么无缝切换的。这些问题,其实回答起来也是比较复杂的。我们今天就从
SpringApplication.run(EasyPaasAdminApplication.class, args);入口,逐渐向下看下执行流程。来试着回答一下前面这两个问题。后面关于SpringBoot 的web容器可以无缝随意切换为jetty,undertow..这个问题的回答涉及到Spring Boot是如何设计WebServer的。我们后续专门讲解一下。
1. 执行逻辑梳理
一般我们SpringBoot 应用的启动入口都是如下这种固定的写法,
也可以是这样
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication application = new SpringApplication(MyApplication.class);
// ... customize application settings here
application.run(args)
}
但总之,都是使用SpringApplication 调用静态方法
此方法的注释
Static helper that can be used to run a SpringApplication from the specified source using default settings.
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class?> primarySource, String... args) {
return run(new Class?>[] { primarySource }, args);
}
跟过来就到这,可以看到注释运行Spring应用程序,创建并刷新一个新的ApplicationContext。

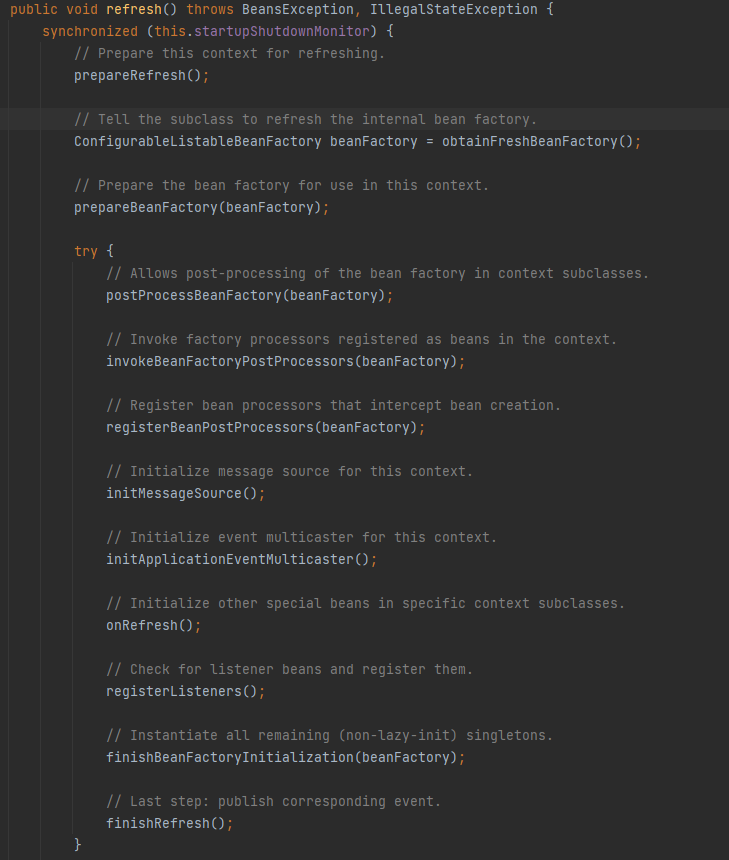
跟代码到这儿其实我们对于SpringBoot 的基本启动流程已经知道了。但是要解答什么时候启动的Tomcat 还需要继续分析。

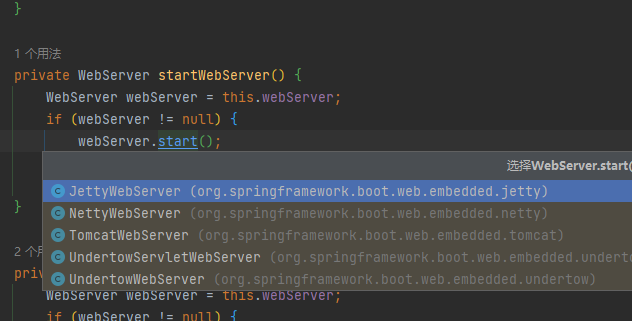
到这儿我们就可以继续下去,发现Spring Boot 启动WebServer。此处的WebServer我就不展开了,可以点击去就三个方法start ,stop,getPort。可以看出来Spring 在设计接口的时候还是很严谨和精简。我们的核心脉络是梳理SpringBoot 启动过程,并且回答Tomcat 是如何被启动的。

我们可以看到WebServer 的实现目前内置的有5种。其实Spring Boot 还有一个特性叫做 自动装配。
这就是为什么5个实现,我们最后启动的是Tomcat。此处也不做展开。后面我专门搞一个解析SpringBoot 自动装配的文章。
我们看一下内部start 的TomcatWebServer的内部实现。了解过Tomcat 源码的同学看到这儿就基本明白了。
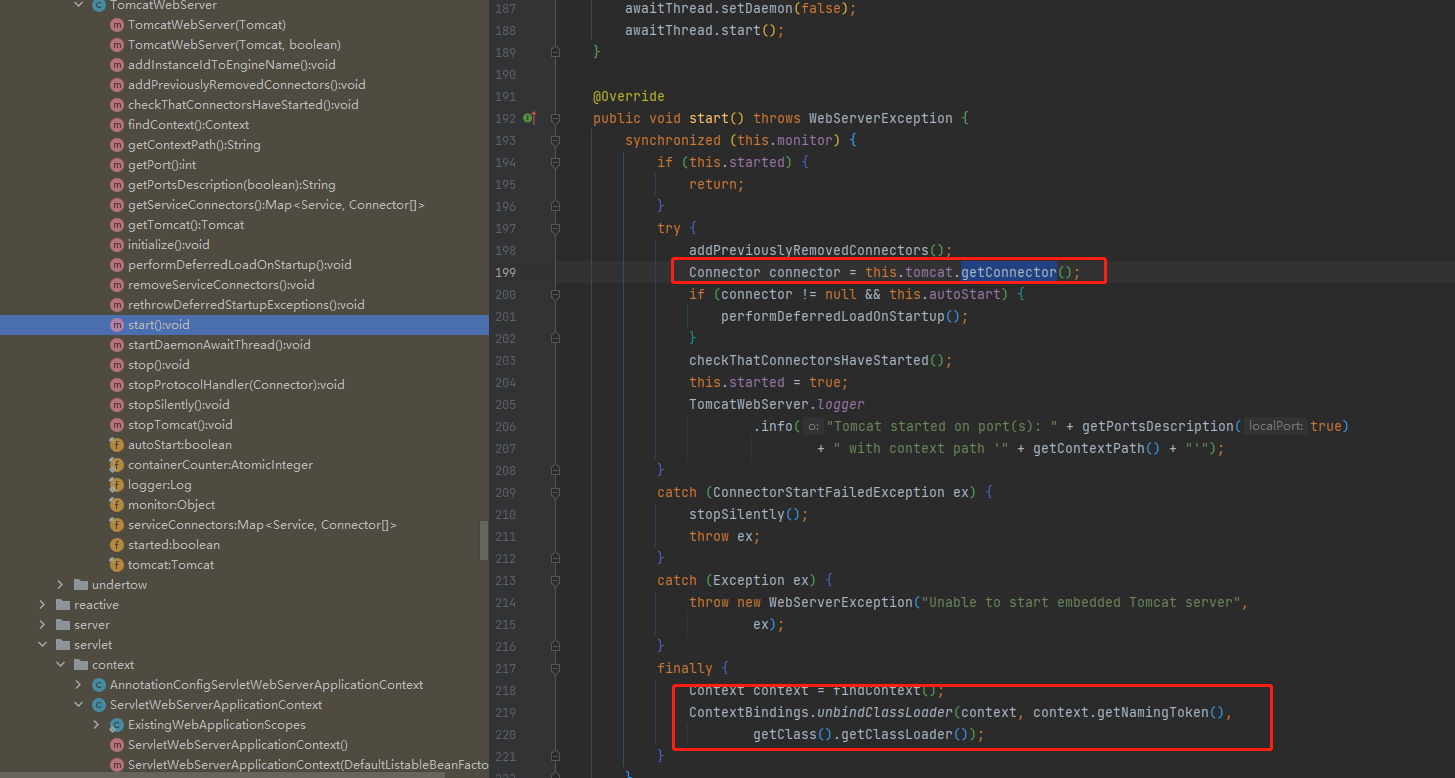
好源码跟进过程我们到此结束,我们整理和总结一下。
通过扫一遍源码我们大概可以总结出来如下三个阶段
准备阶段、应用上下文创建阶段、刷新上下文阶段。
1. 准备阶段: Spring Boot 会加载应用程序的初始设置,并创建 Spring Boot 上下文。这个阶段的核心源码是 SpringApplication 类的 run() 方法,它会调用 Spring Boot 的各个初始化器进行初始化和准备工作。
2. 应用上下文创建阶段 : Spring Boot 会创建应用程序的上下文,包括各种配置信息、Bean 的加载和初始化等。这个阶段的核心源码是 Spring Boot 自动配置机制,通过扫描 classpath 中的配置文件,自动加载和配置各种组件和 Bean。
3. 刷新上下文阶段: Spring Boot 会执行各种启动任务,包括创建 Web 服务器、加载应用程序的配置、初始化各种组件等。这个阶段的核心源码是 Spring Boot 的刷新机制,它会调用各种初始化器和监听器,执行各种启动任务。其中启动Tomcat 就是在这个环节进行。
2. 核心源码解析
既然上面我们已经基本上总结除了,Spring Boot的启动脉络。也梳理出了一些核心源码。那么我们对启动过程的核心源码解析一下。
2.1. 准备阶段
在准备阶段中,Spring Boot 会加载应用程序的初始设置,并创建 Spring Boot 上下文。这个阶段的核心源码是 SpringApplication 类的 run() 方法,它会调用 Spring Boot 的各个初始化器进行初始化和准备工作。
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
// 启动计时器
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
// 定义应用程序上下文和异常报告器列表
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
CollectionSpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList>();
// 配置 Headless 属性
configureHeadlessProperty();
// 获取 Spring Boot 启动监听器
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
// 执行启动监听器的 starting 方法
listeners.starting();
try {
// 解析命令行参数
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
// 准备应用程序环境
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments);
// 配置忽略 BeanInfo
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
// 打印 Banner
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
// 创建应用程序上下文
context = createApplicationContext();
// 获取异常报告器,关于异常报告,我下次专门讲一下SpringBoot 的异常收集器。
exceptionReporters = getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringBootExceptionReporter.class, new Class[]{ConfigurableApplicationContext.class}, context);
// 准备应用程序上下文
prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
// 刷新应用程序上下文
refreshContext(context);
// 刷新后操作
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
// 停止计时器
stopWatch.stop();
// 记录启动日志
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
// 执行启动监听器的 started 方法
listeners.started(context);
// 执行 Runner
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
} catch (Throwable ex) {
// 处理启动失败
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
try {
// 执行启动监听器的 running 方法
listeners.running(context);
} catch (Throwable ex) {
// 处理启动失败
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, null);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
// 返回应用程序上下文
return context;
}
在 run() 方法中,Spring Boot 首先会创建一个 StopWatch 对象,用于记录整个启动过程的耗时。然后,Spring Boot 会调用 getRunListeners(args) 方法获取 Spring Boot 的各个启动监听器,并调用
starting() 方法通知这些监听器启动过程已经开始。 接着调用 prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments) 方法创建应用程序的环境变量。这个方法会根据用户的配置和默认设置创建一个 ConfigurableEnvironment对象,并将其传给后面的 createApplicationContext() 方法。printBanner(environment) 方法打印启动界面的 Banner,调用 refreshContext(context)方法刷新上下文。这个方法会启动上下文,执行各种启动任务,包括创建 Web 服务器、加载应用程序的配置、初始化各种组件等。具体的启动任务会在刷新上下文阶段中进行。
2.2. 应用上下文创建阶段
在应用上下文创建阶段中,Spring Boot 会创建应用程序的上下文,包括各种配置信息、Bean 的加载和初始化等。这个阶段的核心源码是 Spring Boot 自动配置机制,通过扫描 classpath 中的配置文件,自动加载和配置各种组件和 Bean。
protected ConfigurableApplicationContext createApplicationContext() {
Class?> contextClass = this.applicationContextClass;
if (contextClass == null) {
try {
switch (this.webApplicationType) {
case SERVLET:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_SERVLET_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS);
break;
case REACTIVE:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_REACTIVE_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS);
break;
default:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_CONTEXT_CLASS);
}
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Unable to create a default ApplicationContext, " +
"please specify an ApplicationContextClass", ex);
}
}
return (ConfigurableApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
}
在 createApplicationContext() 方法中,Spring Boot 首先会判断应用程序的类型,如果是 Web 应用程序,则会创建一个 WebApplicationContext;否则,会创建一个普通的 ApplicationContext。调用 BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass) 方法创建应用程序的上下文。这个方法会根据上面的逻辑创建一个相应的 ApplicationContext。调用 load() 方法加载应用程序的配置。关于加载应用配置,可以参阅我之前写一篇文章《三分钟了解SpringBoot配置优先级底层源码解析》。这个方法会扫描 classpath 中的各种配置文件,例如 application.properties、application.yml、META-INF/spring.factories 等,自动配置各种组件和 Bean。调用 postProcessApplicationContext() 方法对应用程序的上下文进行后处理。这个方法会调用各种初始化器和监听器,执行各种初始化任务。
2.3. 刷新上下文阶段
在刷新上下文阶段中,Spring Boot 会执行各种启动任务,包括创建 Web 服务器(刚才我们跟源码的时候也看到了,如上我的截图)、加载应用程序的配置、初始化各种组件等。这个阶段的核心源码是 Spring Boot 的刷新机制,它会调用各种初始化器和监听器,执行各种启动任务。
protected void refreshContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext) {
refresh(applicationContext);
if (this.registerShutdownHook) {
try {
applicationContext.registerShutdownHook();
}
catch (AccessControlException ex) {
// Not allowed in some environments.
}
}
}
在 refreshContext() 方法中调用 refresh(applicationContext) 方法刷新上下文。这个方法是 ApplicationContext 接口的核心方法,会启动上下文,执行各种启动任务。调用 registerShutdownHook() 方法注册应用程序的关闭钩子。这个方法会在应用程序关闭时自动执行,清理资源、关闭线程等,所以我们利用此特性在服务关闭的时候清理一些资源。并向外部发送告警通知。
在 refresh(applicationContext) 方法中,Spring Boot 会执行上下文的各种启动任务,包括创建 Web 服务器、加载应用程序的配置、初始化各种组件等。具体的启动任务会调用各种初始化器和监听器,例如:
for (ApplicationContextInitializer?> initializer : getInitializers()) {
initializer.initialize(applicationContext);
}
另外,Spring Boot 还会调用各种监听器,我们不做赘述,例如:
for (ApplicationListener?> listener : getApplicationListeners()) {
if (listener instanceof SmartApplicationListener) {
SmartApplicationListener smartListener = (SmartApplicationListener) listener;
if (smartListener.supportsEventType(eventType)
&& smartListener.supportsSourceType(sourceType)) {
invokeListener(smartListener, event);
}
}
else if (supportsEvent(listener, eventType)) {
invokeListener(listener, event);
}
}
基本上就是这些了。
关于SpringApplication的官方文档讲的比较简单,大家可供参考。地址如下:
https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current/reference/html/features.html#features.spring-application
👏好了,本次的分享就到这儿,我是冰点,下次见。如果我的文章对你有所收获,可以给个赞。如果有疑问可以在评论区留言。


