目录
前言
一、@Component
二、@Repository、@Service、@Controller
三、@Scope
四、@Autowired
五、@Qualifier
六、@Value
1. 直接设置固定的属性值
2. 获取配置文件中的属性值
3. 测试结果
往期专栏&文章相关导读
1. Maven系列专栏文章
2. Mybatis系列专栏文章
3. Spring系列专栏文章
前言
注解配置和xml配置对于Spring的IOC要实现的功能都是一样的,只是配置的形式不一样。
准备工作:
- 创建一个新的Spring项目。
- 编写pojo,dao,service类。
- 编写空的配置文件,如果想让该文件支持注解,需要在bean.xml添加新的约束:
一、@Component
@Component可以代替bean标签
- 作用:用于创建对象,放入Spring容器,相当于
- 位置:类上方
- 注意:@Component 注解配置bean的默认id是首字母小写的类名。也可以手动设置bean的id值。
// 此时bean的id为studentDaoImpl
@Component
public class StudentDaoImpl implements StudentDao{
public Student findById(int id) {
// 模拟根据id查询学生
return new Student(1,"程序员","北京");
}
// 此时bean的id为studentDao
@Component("studentDao")
public class StudentDaoImpl implements StudentDao{
public Student findById(int id) {
// 模拟根据id查询学生
return new Student(1,"程序员","北京");
}
}二、@Repository、@Service、@Controller
作用:这三个注解和@Component的作用一样,使用它们是为了区分该类属于什么层。
位置:
- @Repository用于Dao层
- @Service用于Service层
- @Controller用于Controller层
@Repository
public class StudentDaoImpl implements StudentDao{}
@Service
public class StudentService {}三、@Scope
作用:指定bean的创建策略
位置:类上方
取值:singleton prototype request session globalsession
@Service
@Scope("singleton")
public class StudentService {}测试一下:
@Test
public void t1(){
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
StudentDao studentDao = (StudentDao) ac.getBean("studentDao");
System.out.println(studentDao);
StudentService service1 = (StudentService) ac.getBean("studentService");
System.out.println(service1.hashCode());
StudentService service2 = ac.getBean("studentService",StudentService.class);
System.out.println(service2.hashCode());
}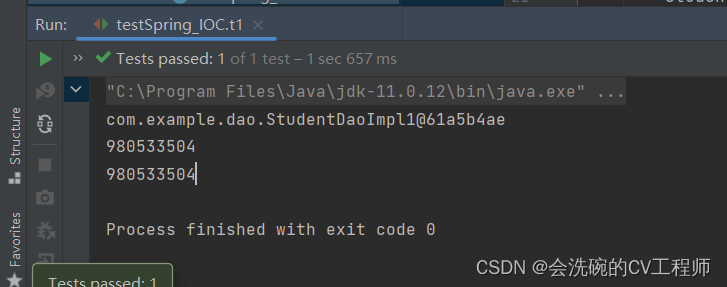
OK,确实可以
四、@Autowired
作用:从容器中查找符合属性类型的对象自动注入属性中。用于代替 中的依赖注入配置。
位置:属性上方、setter方法上方、构造方法上方。
注意:@Autowired 写在属性上方进行依赖注入时,可以省略setter方法。
@Component
public class StudentService {
@Autowired
private StudentDao studentDao;
public Student findStudentById(int id){
return studentDao.findById(id);
}
}
// 测试方法
@Test
public void t2(){
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
StudentService studentService = (StudentService) ac.getBean("studentService");
System.out.println(studentService.findStudentById(1));
}测试结果:
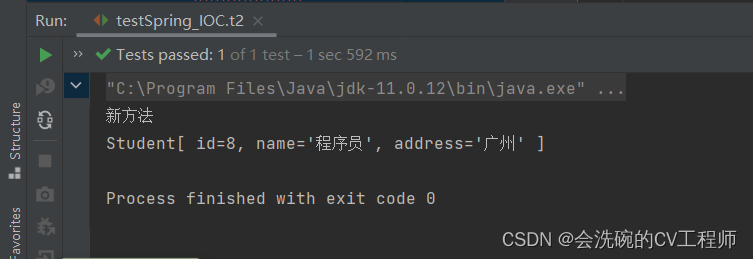
OK,也是可以的
五、@Qualifier
作用:在按照类型注入对象的基础上,再按照bean的id注入。
位置:属性上方
注意:@Qualifier必须和@Autowired一起使用。
如下
@Component
public class StudentService {
@Autowired
@Qualifier("studentDaoImpl2")
private StudentDao studentDao;
public Student findStudentById(int id){
return studentDao.findById(id);
}
}六、@Value
作用:注入String类型和基本数据类型的属性值。
位置:属性上方以下说明一下用法:
1. 直接设置固定的属性值
@Value("1")
private int count;
@Value("hello")
private String str;2. 获取配置文件中的属性值
编写配置文件db.properties
jdbc.username=root
jdbc.password=123456spring核心配置文件(bean.xml)扫描配置文件
注入配置文件中的属性值
@Value("${jdbc.username}")
private String username;
@Value("${jdbc.password}")
private String password;3. 测试结果
测试方法
// 测试注解Value
@Test
public void t3(){
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
StudentService service = ac.getBean("studentService",StudentService.class);
System.out.println(service);
}运行结果
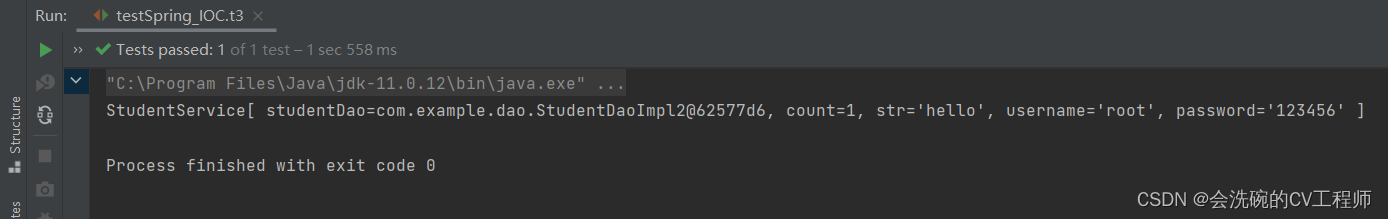
OK,应该和上面设置的值一样,说明可以使用,本篇就介绍到这几个注解了,下篇会介绍完接下来的注解。
往期专栏&文章相关导读
大家如果对于本期内容有什么不了解的话也可以去看看往期的内容,下面列出了博主往期精心制作的Maven,Mybatis等专栏系列文章,走过路过不要错过哎!如果对您有所帮助的话就点点赞,收藏一下啪。其中Spring专栏有些正在更,所以无法查看,但是当博主全部更完之后就可以看啦。
1. Maven系列专栏文章
| Maven系列专栏 | Maven工程开发 |
| Maven聚合开发【实例详解—5555字】 |
2. Mybatis系列专栏文章
| Mybatis系列专栏 | MyBatis入门配置 |
| Mybatis入门案例【超详细】 | |
| MyBatis配置文件 —— 相关标签详解 | |
| Mybatis模糊查询——三种定义参数方法和聚合查询、主键回填 | |
| Mybatis动态SQL查询 –(附实战案例–8888个字–88质量分) | |
| Mybatis分页查询——四种传参方式 | |
| Mybatis一级缓存和二级缓存(带测试方法) | |
| Mybatis分解式查询 | |
| Mybatis关联查询【附实战案例】 | |
| MyBatis注解开发—实现增删查改和动态SQL | |
| MyBatis注解开发—实现自定义映射关系和关联查询 |
3. Spring系列专栏文章
| Spring系列专栏 | Spring IOC 入门简介【自定义容器实例】 |
| IOC使用Spring实现附实例详解 | |
| Spring IOC之对象的创建方式、策略及销毁时机和生命周期且获取方式 | |
| Spring DI简介及依赖注入方式和依赖注入类型 | |
| Spring IOC相关注解运用——上篇 | |
| Spring IOC相关注解运用——下篇 | |
| Spring AOP简介及相关案例 | |
| 注解、原生Spring、SchemaBased三种方式实现AOP【附详细案例】 | |
| Spring事务简介及相关案例 | |
| Spring 事务管理方案和事务管理器及事务控制的API | |
| Spring 事务的相关配置、传播行为、隔离级别及注解配置声明式事务 |


